The Artificial Intelligence (AI) Chronicles
A record of the main historical events in the development of artificial intelligence, the content of which is constantly updated over time for the reference of people in the AI industry.
Phase I: The Birth of Artificial Intelligence (1943-1956)
1943
Turing is known as the father of computer science and the father of the science of artificial intelligence. During World War II, his team successfully developed a machine called "Colossus" in 1943, which was used to break German ciphered telegrams. This contribution brought the end of World War II two years earlier and saved tens of millions of lives.
1946
In 1946, the world's first general-purpose computer, the ENIAC, was born. It was initially developed for the U.S. military and was capable of performing 5,000 additions and 400 multiplications per second, which provided the material basis for the research of artificial intelligence.
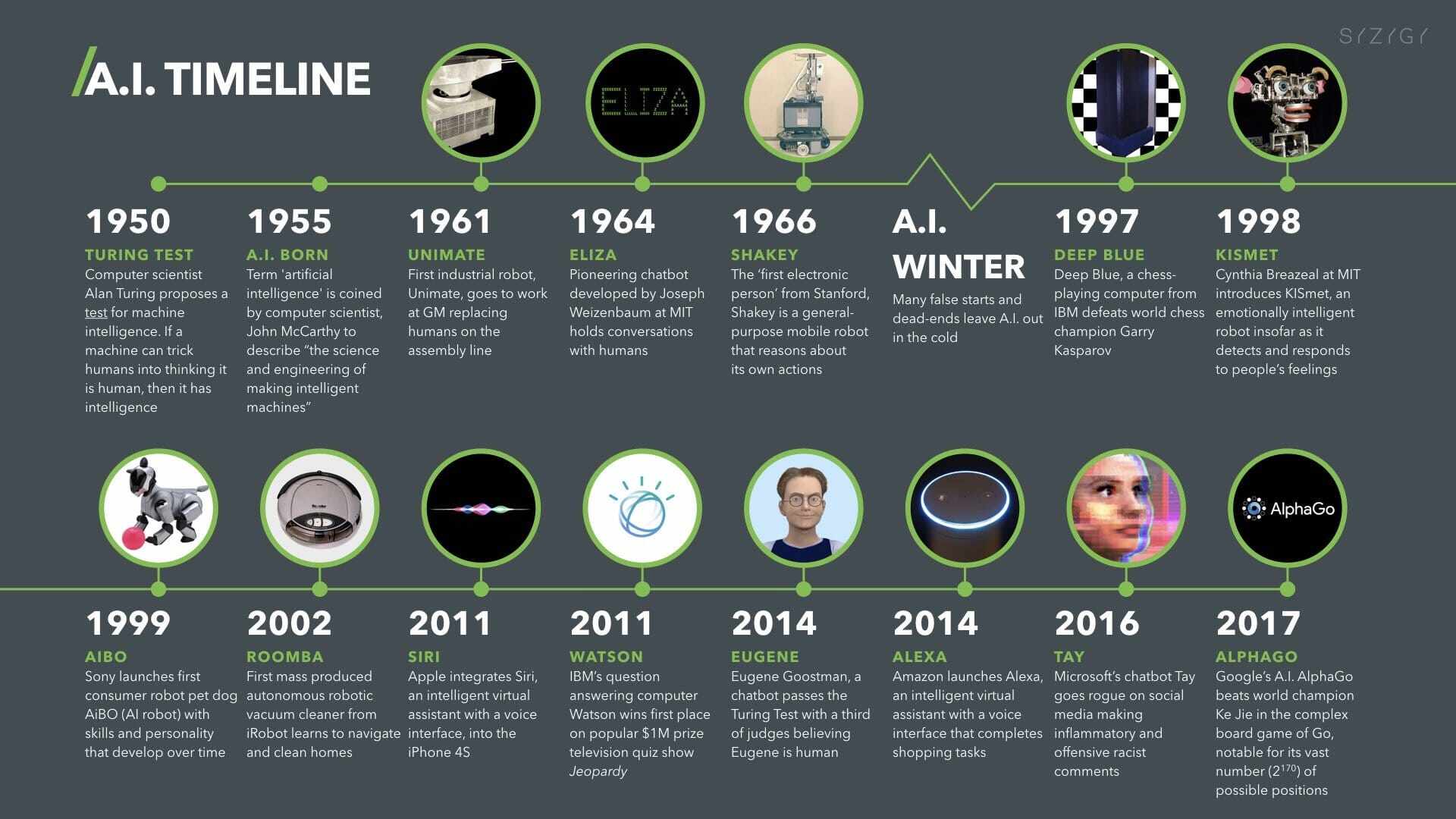
1950
In 1950, a senior named Marvin Minsky (later known as the " Father of Artificial Intelligence ") and his classmate, Dunn Edmunds, built the world's first neural network computer. This is also seen as a starting point for artificial intelligence!
In 1950, Alan Turing introduced the "Turing Test". A computer passes the test if it can answer a series of questions posed by a human tester within 5 minutes, and if more than 30% of its answers are mistaken by the tester for human answers. This aspect of the thesis was the possibility of creating machines with real intelligence.
1956
In 1956, computer expert John McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence". This is seen as the official birth of artificial intelligence. McCarthy and Minsky co-founded the world's first artificial intelligence laboratory - MIT AI LAB.
Phase II: The Golden Age of Artificial Intelligence (1956 - 1974)
1958
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, founded in 1958, invested millions in the field of artificial intelligence, giving computer scientists the freedom to explore new areas of AI technology!
John McCarthy developed the LISP language, which became the predominant programming language in AI for decades to come!
1959.
In 1959, the first industrial robot was born. American inventors George DeVore and Joseph Ingeborg invented the first industrial robot, which issued commands to control a multi-degree-of-freedom machine with the help of a computer that reads schematic stored programs and information. It had no sense of the external environment
In 1959, computer game pioneer Arthur Samuel wrote a checkers program on IBM's first commercial computer, the IBM 701, which successfully defeated then-checkers grandmaster Robert Nirai.
1964.
In 1964, the first chatbot was born. Professor Joseph Weizenbaum of the AI Lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the United States developed the ELIZA chatbot, which realized communication between a computer and a human being through text. This was an important aspect of artificial intelligence research. However, it simply restated the question in a grammatically correct manner.
1965.
In 1965, expert systems made their debut. American scientists such as Edward Feigenbaum developed the chemical analysis expert system program DENDRAL. it was able to analyze experimental data to determine the molecular structure of unknown compounds.
1968.
In 1968, the first artificially intelligent robot was born. Shakey, a robot developed by the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) in the United States, was able to autonomously perceive, analyze its environment, plan its behavior, and perform tasks, and could discover and grasp blocks at the command of Mandarin. This robot has human-like senses such as touch and hearing.
1970
In 1970, systems that could analyze semantics and understand language were born. SHRDLU, a human-robot dialogue system developed by T. Winograd, a computer professor at Stanford University, was able to analyze commands, such as understanding semantics, interpreting unclear sentences, and completing tasks through virtual cube manipulation. Due to its ability to understand language correctly, it was seen as a great success in AI research.
Phase III: The First Low Point of Artificial Intelligence (1974 - 1980)
1973
In 1973, the famous mathematical Rathschilds submitted a research report on artificial intelligence to the British government, which severely criticized the robotics, language processing and image recognition technologies at that time, and pointed out sharply that those seemingly grandiose goals of artificial intelligence could not be achieved at all, and that the research had been a complete failure. Since then, the scientific community has conducted a round of in-depth interrogation of artificial intelligence, so that AI's suffered severe criticism and questions about its actual value.
1976.
In 1976, expert systems were widely used. Stanford University's Shotliff and others released MYCIN, a medical consulting system that could be used to diagnose infectious blood diseases. During this period, expert systems were also developed for manufacturing, financial accounting, finance, and other fields.
At the end of the 1970s, artificial intelligence entered a low point. Researchers underestimated the difficulty of artificial intelligence, the failure of the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's cooperative program, but also let everyone on the prospects of artificial intelligence. The main technical bottlenecks: insufficient computer performance, insufficient ability to deal with complex problems, serious lack of data volume.
Phase 4: The Boom of Artificial Intelligence (1980 - 1987)
1980
In the 1980s, Carnegie Mellon University designed an "expert system" called XCON for Digital Equipment Corporation. It was a computerized intelligence system with complete expertise and experience. It saved the company more than $4,000 a year until 1986!
In the 1980s, a class of AI programs called "expert systems" began to be adopted by companies around the world, and "knowledge processing" became the focus of mainstream AI research. The Japanese government aggressively invested in AI in the same era to promote its fifth generation of computer engineering. Another exciting event in the early 80s was the revitalization of connectionism by John Hopfield and David Rumelhart. ai was once again a success.
1981
In 1981, Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry allocated $850 million to support the Fifth Generation Computer Project. The goal was to build machines that could talk to people, translate language, interpret images, and reason like people. The "turnipists" were unhappy that they chose Prolog as the project's main programming language.
Other countries responded. The United Kingdom began the £350 million Alvey project. In the United States, a business association organized the MCC (Microelectronics and Computer Technology Corporation) to fund large-scale projects in AI and information technology. Computing Initiative, which tripled its 1988 investment in AI from its 1984 level.
1982
In 1982, physicist John Hopfield demonstrated that a new type of neural network (now known as the Hopfield network ) could learn and process information in a completely new way. Around the same time (and before Paul Werbos), David Rumelhart popularized en: Backpropagation, a neural network training method. These discoveries revitalized connectionism, which had been abandoned since 1970.
1984
In 1984, the Cyclopedia Project (Cyc), an attempt to build a giant database of all general knowledge possessed by humans by feeding it into computers, and to implement knowledge-based reasoning on top of it, became a new direction for research and development in the field of artificial intelligence, with the goal of enabling artificial intelligence applications to work in a manner similar to that of human reasoning.
1986
The new field was unified and promoted in 1986 with the publication of the two-volume treatise Distributed Parallel Processing, edited by Rumelhart and psychologist James McClelland, and in the 1990s, neural networks became a commercial success, with applications in optical character recognition and speech recognition software. software.
1987
In 1987, desktop computers made by Apple and IBM surpassed general-purpose computers made by Symbolics and other manufacturers. Since then, expert systems have fallen out of favor, and in the late 1980s, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) senior management decided that AI was not "the next wave".
From then on, AI once again became a sunset red in the vast Pacific Ocean.
Stage 5: The second low point of AI (1987-1993)
The commercial pursuit of AI in the mid-1980s and its fall from grace fit the classic pattern of an economic bubble, the bursting of which was also observed by government agencies and investors in AI. Despite the various criticisms encountered, the field continued to move forward. From the related research field of robotics, Rodney
Brooks and Hans Moravec proposed an entirely new scenario for AI
The earliest sign of the change of heart was the sudden drop in demand for AI hardware in 1987, when desktop computers from Apple and IBM increased in performance, outperforming expensive Lisp machines from Symbolics and others. The old products lost their raison d'être: a half-billion-dollar industry collapsed overnight.
1989
In the late 1980s, the Strategic Computing Initiative drastically cut funding for AI; the new leadership of DARPA believes that AI is not "the next wave" and that grants will go to programs that appear to be more likely to produce results.
1990
In his 1990 paper " Elephants Don't Play Chess," robotics researcher Rodney Brooks proposes the " Physical Symbol System Hypothesis," which holds that symbols are fungible, that symbols are dispensable because "the world is the best model for describing itself. It is always up to date. It always includes all the details that need to be studied. The trick is to perceive it correctly, frequently enough." In the 1980s and 1990s, there were also many cognitive scientists who argued against models of intelligence based on symbolic processing, arguing that the body is necessary for reasoning, a theory known as the " embodied mind/reason/cognition " thesis.
1991
In 1991, it became clear that the Japanese ambitious "Fifth Generation Project" of a decade earlier had not been realized. In fact, some of the goals, such as "starting a conversation with a human being", were not realized until 2010. As with other AI projects, expectations were much higher than what was really possible.
1993
A crisis of trust in both expert systems and AI began to develop, and a strong voice began to question the current direction of AI development, arguing that the top-down approach of programming using rules set by humans was wrong. Elephants don't play chess, but elephants can learn to recognize their environment and make judgments from reality, and AI technology should also have the ability to physically perceive, so that true intelligence can be achieved from the bottom up. This view was ahead of its time, but it also drove the growth and development of subsequent neural network technology
Phase 6: Smooth Transition of Artificial Intelligence (1993-2011)
1995
In 1995, Richard Wallace received inspiration from the 1960s chat program ELIZA and developed the new chatbot program Alice, which was able to use the Internet to continually add to its own data set and optimize its content.
Although Alice doesn't really pass the Turing test either, its design ideas are so far-reaching that the 2013 Oscar-winning film HER (Her) is based on Alice.
1997
In 1997, DeepBlue, IBM's chess computer, defeated World Chess Champion Kasparov. It operates at a speed of 200 million moves per second and holds data on 700,000 games played by grandmasters, allowing it to search for and estimate the next 12 moves!
In 1997, two German scientists, Hockwright and Schmiederheber, proposed Long-term Short-term Memory (LSTM). This is a recurrent neural network that is still used today for handwriting recognition and speech recognition, and has had a profound impact on subsequent research in artificial intelligence.
1998.
In 1998, American companies created Furby, the first pet robot.
As for Japan, which is keen on robotics, in 2000, Honda released its robot product ASIMO, which, after more than a decade of upgrades and improvements, is now one of the most advanced robots in the world.
2001
In 2001, the movie "AI" directed by Spielberg was released. The movie describes the paradoxes of the future world of symbiosis between humans and robots. Artificial intelligence once aroused social concern, but the theme about technology was soon forgotten, and the audience only remembered the sad story about human nature, about love and being loved several years later.
2002
In 2002, iRobot, an American advanced robotics company, launched the Roomba sweeper to the market, which was a huge success. iRobot is still one of the best brands of sweeping machines today!
2004
In 2004, American neuroscientist Jeff Hawkins published the book " The Future of Artificial Intelligence ", which discussed in depth the brand new brain memory prediction theory, and pointed out how to build truly intelligent machines according to this theory. And this book had a profound impact on the subsequent in-depth study of neuroscience.
2006
In 2006, Jeffrey Hinton published Learning Multiple Layers of Representation, which laid the groundwork for the new architecture of neural networks, which is still the core technology for deep learning in artificial intelligence.
2007
In 2007, Feifei Li, a Chinese-American scientist teaching at Stanford, initiated the creation of the ImageNet project. In order to provide a sufficient amount of reliable image data to artificial intelligence research organizations, ImageNet called on the public to upload images and label their contents. ImageNet now contains data of 14 million images in more than 20,000 categories.
2010
Since 2010, ImageNet has held annual large-scale visual recognition challenges, in which developers and research institutions around the world participate by contributing the best AI image recognition algorithms for judging. In particular, the deep convolutional neural network algorithm designed by the University of Toronto at the Challenge in 2012 is considered by the industry as the beginning of the deep learning revolution.
2011
In 2011, Watson participated in a quiz show in which Watson, an artificial intelligence program developed by IBM, competed in a quiz show and defeated two human champions. Watson has stored 200 million pages of data and is able to extract keywords related to a question from seemingly related answers. This artificial intelligence program has been widely used by IBM in the field of medical diagnosis.
2012.
Chinese-born scientist, Ernest Wu and his team began working on large-scale unsupervised machine learning using graphics processors (GPUs rather than CPUs) in 2009, attempting to make AI programs fully autonomous in recognizing the content of graphics.
In 2012, Wu Enda achieved the amazing feat of showing the world a super-powerful neural network that was able to recognize the content of images that contained kittens after autonomously viewing tens of millions of images. This was a landmark event in the history of autonomous reinforcement learning by machines without human intervention.
2014.
In 2009, Google began secretly testing driverless car technology; by 2014, Google became the first company to test a self-driving car in a state that passed the US
2016-2017.
In 2016~2017, AlphaGo defeated the Go champion. AlphaGo is an artificial intelligence Go program developed by Google DeepMind with self-learning capabilities. It is able to collect a large amount of Go game data and celebrity games to learn and mimic human play.DeepMind has entered fields such as healthcare.
In 2017, deep learning was a big hit: AlphaGoZero (the fourth generation of AlphaGo) swept the second version of "Old Dog" 100:0 three days after it started to learn Go on its own without any data input, and beat the third version, which was unattainable for human masters, after 40 days of learning. "Master
Phase 7: The Age of Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models (2017-Present)
2017
Google published the paper "Attention is All You Need", introducing the Transformer architecture, which subsequently became the core of large language models, including OpenAI's GPT-4, sparking the AI revolution.
2018
Amazon.com began developing voice-controlled smart speakers in 2010, and in 2014, officially released the product Echo, a speaker product that can control home appliances and provide informational messages by voice.
Subsequently, Google and Apple have launched similar products, and domestic manufacturers such as Ali, Xiaomi, Baidu, Tencent, etc. have followed suit, and for a time, smart speaker products have blossomed all over the place, and they are all trying to seize the entrance to the user's family living room.
The technology behind the smart speaker is voice assistant, and currently the strongest technology is in the hands of Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Apple and Samsung, and several other giants.
At present, the conventional voice recognition technology is relatively mature, and the pronunciation technology needs to be improved. The real semantic understanding technology is still in a relatively elementary stage, and for the loose and free spoken expression, the voice assistant often can't get the focus, let alone answer correctly.
In 2018, Google released an upgraded demo of its voice assistant, showing a scene in which the voice assistant automatically makes a phone call and completes the owner's task. It included new technologies such as multi-round dialog and full-duplex voice, which may herald the arrival of a new round of natural language processing and semantic understanding technology.
2020.
U.S. artificial intelligence research company OpenAI rises to prominence: in 2020, it releases Jukebox, a neural network, in April; releases GPT-3, a language model, in May; and opens its AI Application Programming Interface (API) in June;
2021.
OpenAI 2021 January release of CLIP, a neural network that connects text and images; March release of DALL- E, a neural network that creates images from text; thus the road to AIGC is officially open, and from the end of 2021 to the beginning of 2022, with the concept of the meta-universe, the virtual digital person also storms the fire;
2022
-
In April, OpenAI upgraded DALL-E 2, once again setting a benchmark for the field of image generation. Ordinary people can help generate the corresponding image by simply inputting a piece of text.
-
August, a piece of AI work produced by the MidJouney tool "Space Opera House" won first place in the human art competition news rushed to the hot search, followed by a few months of Stable Diffusion, Dream Thief, the intention of the inter-AI AI and other AI painting tools have come to the public eye, causing a boom in the use of AI by early mankind.
-
In September, Google Research and UC Berkeley launched the DreamFusion model, which enables the generation of 3D objects from text. This means you can generate 3D images from text descriptions without 3D training data or modifying image diffusion models.
-
On September 29, Meta debuted Make-A-Video, an AI system that generates short videos from given textual cues and does not require pairs of text-video data for training.Make-A-Video utilizes textual cues converted into vector embeddings, which are then further processed by multiple neural networks to ultimately generate videos. These neural networks were initially designed for generating images, to which Meta added a so-called spatio-temporal layer for video generation.
-
On October 6, Google released Imagen Video and Phenaki, the former focusing on video picture quality, with video resolutions up to a high 1280*768, and the latter focusing on video length, capable of generating two-minute-long videos at lower resolutions based on text of around 200 words;
-
On October 7, Google launched a speech generation AI model - AudioLM, which cannot only generate high-quality, coherent speech, but also generate piano music.
-
On November 22, NVIDIA launched Magic3D, a new AI tool that is twice as fast as Google's DreamFusion technology and offers 8 times the high resolution of DreamFusion.
-
On November 30 OpenAI launched ChatGPT, an interactive chatbot program that introduces Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) technology and a reward mechanism compared to GPT-3, and ChatGPT has begun to explode the AI large language model industry, with a monthly jump of 100 million after only two months.
2023
2023 is known as the year of the large language model, in this year, a large number of technology companies released their own large language model, it is not too much to be called the hundred model war, at the same time, the related technology has also had a great development, in the commercial landing began to appear a lot of landing scenes, related keywords:
ChatGPT, Bard, MoSS, GPT-4, ChatGLM, QLoRA, PaLM2, LIMA, Starfire, Wenxin, Tongyi Qwen, Mamba, InternLM-20B, DALL・E 3, Thousands of Sails, RLHF, Prompt, Words Rhinoceros, Mixed Meta, MathGLM, LongLoRA, Meta by Elephant, XAgent, Tiangong, Star, Pangu, CoDi2
January
-
People around the world are trying different ways of asking questions on ChatGPT
-
On January 27, Microsoft's newest model, VALL-E, is a converter-based TTS model that generates speech for any sound by hearing just a three-second sound sample.
-
On the same day, Google released a new AI model - MusicLM. Through the AI model MusicLM, the text and images can be generated directly and automatically to generate music, and a variety of music styles, any music you want to listen to, basically can be automatically generated.
February
-
Yuan Language Intelligence launched ChatYuan, the first large language model of the Chinese language.
-
Google released its next-generation dialogue AI system Bard in advance to benchmark against the popular ChatGPT.
-
Fudan University also released MOSS, a language model with ChatGPT capabilities, and Peking University proposed a new application called ChatExcel that can directly query data information in tables using natural language.
March.
-
OpenAI announced the opening of the ChatGPT API, which can directly call the model gpt-3.5-turbo, which reduces the cost of use by 90% compared to the previous GPT-3.5, which made developers around the world cheer.
-
Meta fired the first shot at open source, taking the lead in open-sourcing the LLaMA series of large language models. LLaMA-13B can outperform GPT-3, which has a reference count of 175 billion, and can run on a single V100 GPU.
-
Google released PaLM-E, a 562 billion parameter embodied multimodal language model; specifically, PaLM-E-562B integrated PaLM with 540B parameters and Visual Transformer (ViT) with 22B parameters, making it the largest vision-language model known at the time.
-
OpenAI released the GPT-4 multimodal large language model, which once again triggered the world.
-
Baidu released the Wenxin Yiyin large language model product.
-
Tsinghua released ChatGLM.
-
Stanford released the alpaca large language model, Alpaca.
-
Microsoft Bing was strengthened again, accessing the OpenAI DALL-E model and realizing the upgrade of the Wensheng diagram;
-
NVIDIA released a ChatGPT-specific GPT, which can increase the inference speed by 10 times.
In the field of academic research, people gradually began to pay attention to artificial reinforcement learning RLHF, automated neural network pruning, and more in-depth consideration of the application of large language models such as ChatGPT.
April.
-
New open source models continue to be released, technology companies and research institutions continue to make efforts, people are gradually starting the application of large language models and applying the state-of-the-art GPT-4 to the training of new models, and large language models are moving from the stage of open source prohibited commercialization to the stage of open source commercialization;
-
The University of California announced the open-source model Baize, which can run on a single GPU.
-
UC Berkeley's release of the conversation model Koala, which can run on consumer GPUs, where Koala uses conversation data collected from the web to fine-tune LLaMA models.
-
Ali's release of its own large language model of Tongyi Qwen;
-
The release of the open-source project AutoGPT, an experimental open-source application that demonstrates the capabilities of the GPT-4 language model, has also exploded across the web, with STAR exceeding 100,000. The program is driven by GPT-4 and can autonomously achieve any goal set by the user.
-
Microsoft open-sourced DeepSpeed Chat, which allows us to train high-quality large language models similar to ChatGPT at a lower cost and faster speed.
-
Subsequently, Amazon's high-profile entry into the large language model war, the release of the Titan large language model, AI programming assistant, all free.
-
Fudan MOSS-16B was open-sourced and added several new features.
-
LLaVA, a multimodal large language model released by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Microsoft Research, and Columbia University, although LLaVA was trained with a small dataset of multimodal instructions, it demonstrated very similar inference results to the multimodal model GPT-4 on some examples;
-
Stanford Developers released Lamini for developers to quickly build customized models using base models from many companies and organizations.
-
Databricks released Dolly 2.0, the industry's first open-source, directive-following LLM that fine-tunes a transparent and freely available dataset that is also open-source and commercially available, "marking the move from the open-source prohibited-commercial phase of big-model development to the open-source commercial phase.
May.
-
Domestic KU Xunfei released its own Starfire Big Model.
-
Ali Dharma Institute released the multimodal large language model Owl mPLUG-Owl.
-
Google, in order to benchmark GPT-4, released the PaLM second-generation model, which supports multiple languages, stronger math, and code capabilities.
-
Microsoft continued to release Windows Copilot at the Build conference, introducing ChatGPT capabilities to the Windows operating system, aiming to provide users with an efficient personal assistant.
-
Benchmarking Microsoft's Bing conversational search, Baidu announced its own AI search engine, as well as the Wenshin Qianfan large language model platform, which is the world's first one-stop enterprise-level large language model production platform.
-
Meta published the LIMA paper, which performs supervised learning on 1,000 selected samples, and without using the RLHF method at all, LIMA shows very strong performance and generalizes well to tasks beyond training data.
-
Stanford University proposed the AlpacaFarm simulator. AlpacaFarm can replicate the RLHF process in 24 hours for only about $200, allowing open-source models to rapidly improve human assessment results, and can be called a pincushion for RLHF.
-
Researchers from Peking University, Westlake University, and other institutions jointly proposed PandaLM, a new large language model evaluation paradigm that validates large language model capabilities with automated and reproducible testing by training a large language model specifically for evaluation.
June.
-
OpenAI improved the mathematical reasoning capability of GPT-4;
-
Beijing Zhiyuan released the Wudao 3.0 large language model series and entered a new phase of full open source.
-
Google went online with its large language model cloud service, which enables code generation, PaLM2, and other related services to be invoked.
-
Baidu Wenshin Big Model was officially upgraded from 3.0 to 3.5, which not only realizes a comprehensive upgrade in creation, Q&A, reasoning, and code capabilities, but also significantly improves security and training, and reasoning speed.
-
Shangtang Technology and Shanghai AI Lab, in conjunction with the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Fudan University, and Shanghai Jiaotong University, released a 100-billion-parameter large language model, " Shusheng・Pu Language " (InternLM);
-
TII open-sourced a 40-billion-parameter causal decoder model, Falcon-40B, which crushes LLaMA-65B, which has 1.5 times the parameter size, and also outperforms open-source large language models such as MPT, RedPajama, and StableLM;
-
Meta has introduced MusicGen, a text-based music generation model, and it is free for non-commercial use.
-
Researchers at UC Berkeley open-sourced a project, vLLM, which focuses on fast LLM reasoning and services.
-
Stanford has proposed FrugalGPT, a simple and flexible instantiation of cascaded LLM that rivals the performance of the best individual LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) at up to 98% lower cost;
-
Researchers at the University of Washington, ETH Zurich, and other institutions have proposed a new compression format and quantization technique, SpQR (Sparse-Quantized Representation), which, for the first time,e achieves near-lossless compression of LLM across model scales;
-
Institutions such as CAS and Hong Kong Polytechnic have built a table assistant, SheetCopilot, which can quickly connect to various table processing software and support multi-table operation, chart drawing, and pivot table generation.
July
Big models formally entered the open source commercial stage, and the application of large language models gradually began to precipitate into specific application scenarios, and researchers began to release research on the basic capabilities of models.
-
Meta releases the Llama 2 family of models, which includes 7, 13, and 70 billion parameter variants. Llama 2 outperforms other open-source language models in a number of external benchmarks, including inference, coding, proficiency, and knowledge testing, and most importantly, can support commercial applications.
-
Stability AI and CarperAI lab's two large language models, FreeWilly 1 and FreeWilly 2, outperformed Meta's release of Llama-2-70 b-hf and managed to top HuggingFace's Open LLM charts.
-
Jingdong launched the industry-oriented Yanhiru Big Model and Yanhiru AI development computing platform, taking a big step towards the industry.
-
Microsoft empowered the Office family bucket with GPT-4 and announced the pricing.
-
Jiaogong open-sourced the first self-developed domestic comprehensive transportation large language model-TransGPT, which can be commercialized free of charge after applying for and obtaining an official commercial license by email only.
-
Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Computing launched a multilingual large language model, BaiLing, which realizes multilingual human-computer interaction capabilities in a budget-friendly and memory-saving way.
-
Huawei Noah launched its code large language model PanGu-Coder, which dramatically outperforms models of the same parameter size in terms of the one-time pass rate (PASS@1) metrics of code generation, and even outperforms models of larger size.
-
Peking University released its large language model ChatLaw, which topped the Zhihu hot search list.
August.
-
Meta AI launched an OCR tool, named Nougat, which is built on the Transformer model and can easily convert PDF documents to MultiMarkdown.
-
Meta based on Code Llama's latest version of the model WizardCoder 34B, which utilizes Evol-Instruct for fine-tuning and became in HumanEval pass@1 reached an amazing 73.2%, beyond the original GPT-4.
-
Shanghai Qingyuan designed a data selector, selected 200 data points, and then trained the InstructionGPT-4 model, which outperformed MiniGPT-4 with more fine-tuned data.
-
Abacus.AI's research team proposed the truncation strategy, which enables LLaMA2 context length to support 32K context length.
-
Microsoft proposed TinyMIM, which uses distillation to migrate knowledge from large language models to small models while keeping the ViT structure unchanged and without modifying the structure to introduce other inductive biases.
-
The five large language model products in Beijing are Baidu's "Wenxin Yiyin", Jitterbug's "Skylark", and Baichuan Intelligence's "Baichuan Big Model";
-
Tsinghua-based AI company Zhipu Huazhang's "Zhipu Qingyin" and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' "Zidong Taichu";
-
Shanghai's three large language model products include Shangtang's "Negotiation SenseChat", MiniMax's "ABAB Large language model", and Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory's "Shusheng Universal Large language model".
-
The approved companies in Guangdong are Huawei and Tencent, and the KDDI department has approved products in other regions.
September
-
Microsoft large language model Copilot officially embedded in the Windows 11 operating system; Kingsoft Office announced that the intelligent office assistant WPS AI based on the large language model has been accessed to its full range of products, and became the first company to apply the large language model (LLM) in the field of office software, and really delivered a usable product.
-
Ant Group officially released the industrial-grade financial grand model ( AntFinGLM ) at the Bund Conference, and at the same time opened up the financial exclusive task assessment set.
-
Fudan University released DISC-MedLLM, a Chinese medical and healthcare personal assistant. The model's performance in single-round Q&A and multi-round dialog medical and healthcare consulting evaluations showed significant advantages over existing medical dialog large language models.
-
Baidu released the newly upgraded Intelligent Cloud Qianfan Big Model Platform 2.0, which includes four highlights: the largest number of supported large language models and datasets, the most complete toolchain, the best arithmetic performance, and enterprise-grade security.
-
The AI development computing platform of Jingdong Cloud is online, and in less than a week, it can complete the whole process from data preparation, model training, to model deployment; Colossal-AI is iterating again, providing out-of-the-box LLaMA2 training, fine-tuning, and inference solutions from 8 to 512 cards, accelerating the training of 70 billion parameters by 195%, and providing a one-stop cloud platform solution, which can greatly reduce the cost of large language model development and landing applications.
-
OpenAI officially launched DALL・E 3, an AI tool for Venn diagrams, which understands nuances and details better than previous systems, making it easier for users to transform their ideas into very accurate images.
-
A French AI startup, Mistral AI, has released a new model, Mistral 7B, which outperforms Llama 2 13B in every benchmark and outperforms LLaMA 134B in terms of code, math, and reasoning.
-
Tencent formally unveiled the Hybrid Big Model, a large language model with over 100 billion parameters, which gains powerful Chinese authoring capabilities, logical reasoning in complex contexts, and reliable task execution with a number of unique technical capabilities.
-
Meta introduced AnyMAL, a collection of multimodal encoders trained to transform data from a variety of modalities, including image, video, audio, and IMU motion sensor data, into the text embedding space of the LLM.
-
Berkeley, California, open-sourced vLLM, which uses a newly designed attention algorithm, PagedAttention, that allows service providers to easily, quickly, and inexpensively distribute LLM services.
-
Shanghai AI Lab and others formally launched InternLM-20B, a 20 billion parameter version of the Shusheng-Pu Language Large language model (InternLM), which was open-sourced and premiered in the Aliyun Magic Hitch community (ModelScope).
-
Tsinghua University and other researchers jointly proposed MathGLM, a new model that can perfectly perform complex arithmetic operations. The 2 billion-parameter language model is able to accurately perform multi-digit arithmetic operations with an accuracy rate of almost 100% and without data leakage.
-
Zhu Jun and Chen Keyfei's team at Tsinghua University proposed a 4-bit optimizer for neural network training, which saves the memory overhead of model training and, at the same time, achieves an accuracy comparable to that of a full-precision optimizer. The memory overhead of fine-tuned LLaMA-7B can be reduced by up to 57% while maintaining the accuracy without loss.
October
-
Baidu officially launched Wenxin 4.0, which has significantly improved the four major capabilities of comprehension, generation, logic, and memory over the online version of Wenxin Yiyin, and the overall level is no less than that of GPT-4;
-
KU Xunfei officially launched Xunfei Starfire Cognitive Grand Model 3.0 version, and announced that Starfire V3.0 has realized all-around surpassing of ChatGPT in Chinese, and realized benchmarking in English.
-
Tencent announced the upgrade of the hybrid grand model and the official launch of the text-to-graph capability. Wizi Engine released Chatimg 3.0, a multimodal meta-multiplying image, which also supports functions such as multi-diagram comprehension, object localization, OCR, and so on.
-
Wisdom Spectrum AI released ChatGLM3, the third-generation dialog large language model developed by itself, realizing a series of brand-new capabilities, including cross-modal, Agent, and so on.
-
Cambridge, Huawei, etc. released the MetaMathQA dataset, based on LLaMA-2 fine-tuning to get the big language model MetaMath focusing on mathematical reasoning (forward and reverse), and reached SOTA on the mathematical reasoning dataset.
-
Mila et al. propose a new framework called Hypotheses-to-Theories (HtT), which is a new approach that not only improves multi-step reasoning, but also has the advantages of being interpretable and transferable.
-
Meta proposes a new method that effectively extends the contextual capabilities of the underlying model, and the performance of long context LLMs constructed with this method outperforms all existing open-source LLMs.
-
SSEU launched a new value alignment assessment tool: Auto-J, which aims to provide more transparent and accurate model value alignment assessment for the industry and the public.
-
Baichuan Intelligence officially released Baichuan2-192K Long Window Large language model, which increases the length of the context window of Large Language Model (LLM) to 192K tokens in one go.
-
The Ant AI Infra team revisited the loss function of SAM and proposed a more general and effective method, WSAM, which improves the flatness of training extreme points by including flatness as a regularization term.
-
MIT, in joint research with the Chinese University of Hong Kong, proposed LongLoRA. It is an effective fine-tuning method that scales the context size of pre-trained large-scale language models with limited computational cost;
-
Microsoft and other researchers jointly released LLaVA-1.5. With a simple modification of the original LLaVA, and using only 1.2 million publicly available data points, LLaVA-1.5 was trained on a single 8-A100 node in less than 1 day and refreshed SOTA on 11 benchmarks;
-
Microsoft AutoGen framework fires out of the ring, with the number of star tags increasing wildly from 390 to 10K, allowing multiple LLM intelligences to solve tasks by chatting, and the intelligences can play various roles, such as programmers, designers, or a combination of roles, and the conversation process solves the task;
-
Facade Intelligence launched BigModel-XAgent in conjunction with Tsinghua University. XAgent is a new AI model that can realize autonomous solutions of complex tasks, with LLM as the core, able to understand human commands, make complex plans, and take actions autonomously.
November.
-
OpenAI announced a major update to ChatGPT, and its GPT-4 Turbo, with a new large language model that is smarter, has a higher text processing ceiling, is cheaper, and an app store opens.
-
Kunlun Wanwei's big language model, Skywork-13B series, was officially announced as open source. The release of Skywork-13B series can be said to be another masterpiece of an open-source large language model.
-
Ali's Tongyi Qianqian Qwen-72B open source, as of now, there are 1.8B, 7B billion, 14B, 72B reference numbers of four basic open source models, as well as cross-language, image, speech, and other modalities of a variety of open source models;
-
China Telecom's Star Series of Big Models received the latest upgrade. The Star Semantic Big Model formally released a 100 billion parameter version, which significantly improves both inference and answer accuracy, and mentions the context window to 96K Tokens, with a 40% reduction in the phantom rate.
-
Tsinghua introduced LCM/LCM-LoRA (Latent Consistency Model), LCM generates high-resolution images with only a few steps of reasoning, improving the efficiency of mainstream literate graphical models by 5-10 times.
-
Meta proposes EMU VIDEO, which enhances diffusion-based text-to-video generation conditioned on video generation beyond Gen-2 by explicit intermediate image generation steps.
-
Meta proposes a radically different approach to attention mechanisms, whereby attention is enforced by using the LLM as a natural language reasoner, and S2A produces more factual and less obstinate or flattering LLMs than standard attention-based LLMs.
December.
-
Launch of Mamba, a new architecture that promises to disrupt Transformer, rivaling or even beating Transformer in language modeling, scaling linearly with context length, improving performance to million token length sequences, and achieving a 5x improvement in inference throughput.
-
Google's release of Gemini, a native multimodal macromodel.
-
Researchers at Huawei Noah and other organizations have proposed the Pangu-Agent framework, which aims to develop multi-tasking intelligences (Agents) that can solve and adapt to complex tasks.
-
Racer open-sourced the KwaiAgents Intelligent Body Framework, which enables even "small" large language models of 7B/13B to achieve results beyond GPT-3.5, and these systems, models, data, and reviews are open-sourced!
-
UC Berkeley, Microsoft upgraded CoDi to CoDi-2, a versatile, interactive multimodal large language model (MLLM). CoDi-2 is capable of context learning, reasoning, chatting, editing, and other tasks in an any-to-any input-output modal paradigm.
-
Microsoft's announcement that its own small-sized model, Phi-2 (2.7 billion parameters), will be fully open-sourced, with significant performance improvements in commonsense reasoning, language understanding, and logical inference.
-
Huawei released CodeArts Snap, an intelligent development aid for large language models. Based on the powerful understanding and generation capabilities of large language models, CodeArts Snap has eight core capabilities: code generation, R&D knowledge Q&A, unit test case generation, code interpretation, code annotation, code debugging, code translation, and code inspection.
2024
If 2023 is the year of the large language model, 2024 may be designated as the year of the commercialization of the large language model, which will begin to take hold in various industries.
February.
-
On February 2, representatives from 27 EU countries voted unanimously in favor of the text of the Artificial Intelligence Bill, marking an important step towards legislating AI in the EU.
-
February 15, OpenAI launched a new video generation model Sora, 1-minute Vincennes video effect is stunning, Sora compared to other previous Vincennes video model, has crossed over to the practical productivity tools, 1-minute length is expected to be applied on a large scale in the field of short videos, the ability to extend the video is also expected to produce long videos, or will bring a new round of content creation industry revolution.
March
-
On March 4, Anthropic, an AI startup jointly supported by Google and Amazon, released the heavy news that the company launched the next generation of large language model Claude 3 series products, which is comparable to human performance in performing complex tasks, and has become one of the most powerful AI large language model.
-
On March 6, the world's first AI movie, " Terminator 2 - Judgment Day," premiered in the U.S. The movie was made by 50 AI artists with the help of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, Midjourney, Runway, Eleven Labs, and others, and took only 3 months.
-
On March 13, AI startup Cognition released Devin, the world's first "AI software engineer", an AI software engineer that can autonomously learn unfamiliar technologies and automatically carry out activities such as cloud deployment, underlying code, bug fixing, training, and fine-tuning AI models.
-
On March 14, the Microsoft team released AutoDev, an AI programmer. autoDev is designed for autonomous planning and execution of complex software engineering tasks, as well as maintaining privacy and security in Docker environments. Users can define complex software engineering goals, which AutoDev assigns to autonomous AI intelligences to achieve. These AI intelligences can perform a variety of operations on the codebase, including file editing, retrieval, build process, execution, testing, and git operations.
-
On March 18th, Moonshot AI (Dark Side of the Moon) announced that its intelligent assistant Kimi's context window has been boosted to 10x and supports 2 million words of ultra-long, lossless context with immediate effect.
-
On March 22, Ali Tongyi Qianqi was heavily upgraded to open the function of 10-million-word-long document processing for all people for free, becoming the first AI application in the world in terms of document processing capacity.
April
-
April 11, Google Cloud Next conference day, the "European version of OpenAI" Mistral AI released MoE large language model Mixtral 8x22B, the model parameter size of up to 176 billion, becoming the second largest open source parameter size on the market.
-
On April 28, Baidu launched its own AI model "Wenxin Yiyin 3.0", which made a major breakthrough in Chinese understanding and generation, with an accuracy rate of 98%, helping Chinese AI applications to occupy a larger share of the global market, and promoting the upgrading of Chinese content creation, intelligent customer service and other industries.
May
-
May 5, Apple acquired AI startup "VocalIQ", which focuses on speech recognition and natural language processing technology. The acquisition will accelerate Apple's growth in the field of intelligent voice assistants, enhance Siri's interactive experience and level of intelligence.
-
On May 18, the world's first AI medical image diagnostic platform "MediVision" was formally launched, jointly created by a number of top hospitals and AI enterprises, which can quickly and accurately identify a variety of disease images, assisting doctors to improve diagnostic efficiency and accuracy, and promote the clinical application and popularization of medical AI.
June
-
On June 12, Amazon launched the "AWS AI Canvas" service, which provides a one-stop AI application development and deployment platform for enterprises, simplifies the AI model development process, reduces the threshold of enterprise AI applications, and assists the digital transformation and intelligent upgrading of various industries.
-
On June 25, AI made a major breakthrough in the field of scientific research, and the AI model cooperated by a multinational scientific research team successfully predicted the structure and properties of a new type of superconducting material, which opens up a new direction in the research and application of superconducting materials, and accelerates the process of discovery of new materials.
July
-
On July 10, Tesla released a new-generation autopilot AI chip "FSD 4.0", with the arithmetic power increased to 100 trillion times per second, which further enhances the perception and decision-making ability of the autopilot system, pushes the development of unmanned driving technology to a higher level, and injects new impetus for the transformation of intelligent transportation and the automotive industry.
August
-
On August 3, AI achieved another success in the field of artistic creation, and the symphonic work "Song of AI" composed by AI was premiered at the International Music Festival, which won wide acclaim, demonstrating the great potential of AI in music creation, arranging and performance, and bringing new possibilities for the development of music and art.
-
On August 15, the world's first AI smart factory "FutureFab" was put into production, adopting full-process automation and intelligent production system, increasing production efficiency by 30%, and significantly improving product quality and consistency, marking an important step towards the era of intelligent manufacturing in the manufacturing industry.
September
-
On September 5, the United Nations released the Global AI Ethics Guidelines, which aims to regulate the development and application of AI technology, protect personal privacy, promote fairness and justice, and prevent misuse, providing an important ethical framework and guiding principles for global AI governance, and promoting countries to strengthen AI ethical regulation and international cooperation.
October
-
On October 10, Google DeepMind launched a new AI model "AlphaFold 3", which has made revolutionary progress in protein structure prediction, with an accuracy rate as high as 95%, providing a powerful tool for biomedical research, new drug development and other fields, and accelerating the process of exploring life sciences.
-
On October 20, the application of AI in the financial field made a major breakthrough, and the AI investment advisor system "RoboAdvisor" jointly developed by a number of financial institutions was put on line, which can accurately analyze the market trends and risks, and provide users with personalized investment advice and asset management solutions, and promote the intelligent transformation of the financial industry! .
November
-
On November 2, the world's first AI newsroom "AI Newsroom" was established, which was built by a number of media organizations and AI enterprises, adopting AI technology for news gathering, editing and publishing, significantly improving the efficiency and quality of news production, bringing new changes and development opportunities for the news industry.
-
On November 15, AI made significant progress in the field of education. SmartEdu, a personalized AI learning platform jointly developed by the education sector and AI enterprises, was launched on the Internet, which is capable of providing personalized learning programs and tutoring according to students' learning conditions and abilities, and contributing to the fairness and improvement of the quality of education.
-
On November 25, Anthropic launched MCP (Model Context Protocol), an open standard designed to unify communication protocols between large language models (LLMs) and external data sources and tools.
December.
-
On December 8, AI plays an important role in the field of environmental protection. EcoGuard, an AI environmental monitoring system developed by scientific research institutions and environmental protection organizations, was put into use, capable of monitoring and analyzing environmental data in real time, providing early warning of environmental risks, providing scientific basis for environmental protection decision-making, and promoting the construction of ecological civilization.
-
On December 20, the global AI technology summit "AI World 2024" was held in New York, attracting top scientists, entrepreneurs and policy makers in the field of AI from all over the world to discuss the future development of AI technology, industrial applications and ethical governance and other issues, which points out the direction of the global AI cooperation and development! .
2025.
The year 2025 will be the year of Agentic AI, a technology that shifts from "augmented knowledge" to "augmented execution", driving a high degree of automation in human decision-making and operations, and redefining enterprise productivity and human-computer interaction.
January
-
On January 20, 2025, Chinese startup DeepSeek launched DeepSeek-R1, an open-source large language model. The technological breakthrough of "extremely low cost versus top performance" once again blew up a storm in the AI world, sweeping the globe, and became the hottest topic of discussion in the Spring Festival of 2025, in addition to Nezha 2, which was the most popular topic of discussion. It has become the most popular topic of the Spring Festival of 2025, except for Nezha 2.
AI, Big Data, Cloud Computing, and the ongoing IoT (Internet of Things) are the main themes of the second decade of the 21st century.
